Almighty Effluent Treatment Machine (AETM)
Background of the Invention
The environmental pollution created by industrial effluent and municipal sewage has been a serious concern in the past few decades. Most industries discharge their huge volume of effluent to the environment without following the stipulated norms and standards. The growing urbanization and increased living standards of people cause huge generation of municipal sewage, which poses detrimental impact on the environment. On the other hand, the world is facing severe water crisis both in domestic and agricultural sectors. These issues are being put under top priority in the global sustainable development goals. A viable solution to this crisis is to adopt efficient and sustainable methods of wastewater treatment and recycling. In the conventional wastewater treatment method, the effluent is exposed to open air for a long period of time in large on-ground pits constructed over a large area. This system is highly expensive, time-consuming, and environmentally unfriendly; it also requires continuous monitoring throughout the process. This situation calls for off-ground, compact, efficient, rapid, affordable, user-friendly, and sustainable effluent/sewage treatment technologies. By addressing this challenge, the Almighty Engineering team has developed our ground-breaking off-ground technology named Almighty Effluent Treatment Machine (AETM) with the above features.AETM Review Team
Various industries produce effluents that cause land and air pollution. To save water resources and control land pollution, Government has setup some rules for the safe effluent discharge to land and other water resources. While most large-scale industries have their own treatment plants, the small and medium scale industries find it unaffordable. Consequently, the Government has come up with the solution of Common Effluent Treatment Plant (CETP). Accordingly, a minimum of 10 small and medium scale industries are combined to set up CETPs in government-approved areas. The treated effluent can be either disposed of or reused. However, CETP has the following drawbacks
- Requires large space
- Treats only large quantities
- Requires skilled labor
- Requires high initial and operation & maintenance costs
- Requires high electric power
To overcome these drawbacks, AETM has been developed by applying 4R’s (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover), and it offers the following advantages over the existing on-ground technologies:
Salient Features of AETM

User-friendliness

Automation

Quantity

Ease of Maintenance

Cost Reduction
Process Upgradation
AETM Design Considerations
Quality: The treatment processes are designed after testing the effluent/sewage sample characteristics. The treatment processes include the following four stages:

Preliminary Treatment

Primary Treatment

Secondary Treatment

Tertiary or Advanced Treatment
Quantity: The industrial effluent generated per day (or flow rate) helps to determine the size of the AETM for achieving the required quantity of treated water.
Cost: Since the costs of fabrication, installation, operation and maintenance are drastically reduced, our AETM technology can save about 50% compared to the conventional on-ground treatment methods.
Steps in AETM Design & Delivery
- Collecting sample effluent
- Testing the effluent characteristics
- Selecting the appropriate treatment processes
- Designing AETM
- Fabricating AETM
- Demonstrating AETM operation
- Testing the output characteristics
- Delivering AETM to the end user
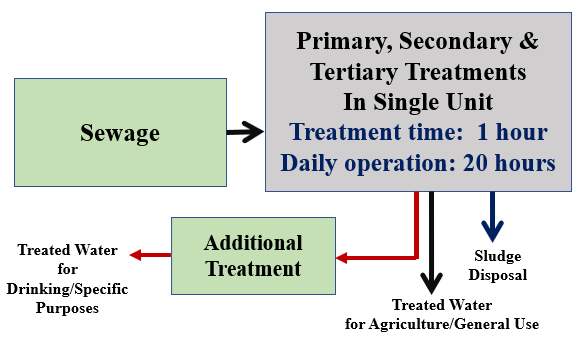
AETM Municipal Sewage Treatment
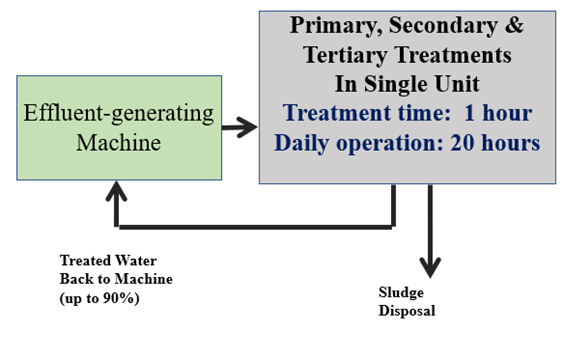
AETM Industrial & Oil Refinery Effluent Treatment
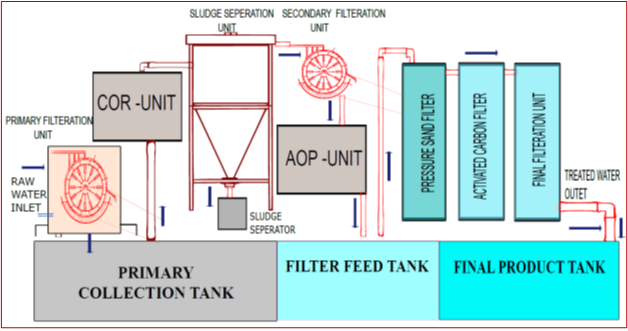
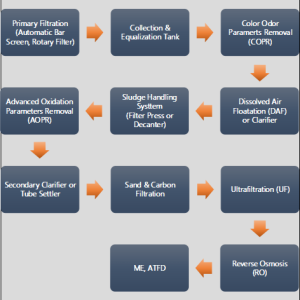
AETM Basic Layout
AETM Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Process
(Additional parameters will be considered depending on the effluent characteristics and client requirements)
| Parameter | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 10-12 mg/l | Neutral |
| COD | Up to 50000 mg/l | Less than 250 mg/l |
| BOD | Up to 7500 mg/l | Less than 30 mg/l |
| TDS | Up to 20000 | As per raw effluent TDS |
| TSS | Up to 1200 mg/l | Less than 30 mg/l |
| Total Hardness | 1500 mg/l | Less than 300 mg/l |
AETM Case Study 1: Textile & Dyeing Effluents
Our AETM technology has unique features that provide compact effluent treatment solutions to all kinds of effluents. Though the nature of effluents from different industries varies depending on the processes and chemicals used, the effluent has few common characteristics. For instance, the textile and dyeing units’ effluent has a characteristic color along with high chemical oxygen demand. AETM provides technologically sound, and economically viable automated smart solution for treating the textile and dyeing industry effluents and offers the following solutions:
AETM uses the following treatment methodologies for textile and dyeing effluents:
Textile and dyeing raw and treated effluent characteristics
| Parameter | Characteristics | Permissible Limit as per Govt. Norms | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Effluent | Treated Water | ||
| pH | 9.71 | 6.6-7.5 | 6 – 8 |
| COD mg/l | 3200 | 100 | 250 |
| BOD | 600 | 20 | 50 |
| TSS | 350 | 15 | 100 |
| Total hardness (ppm) | 300 | 40 | 60 |
| TDS | 7800 | 100 | 2100 |
| Color | 640 | 5 | 15 |
The pH value is an indicator of acidity/alkalinity/neutrality. If pH lies in the range of 6.5 to 7.5, it is considered neutral. The input of the raw effluent was alkaline (pH>7), and upon treatment, the effluent has been neutralized with a pH of 7. The COD value has shown tremendous decrease from 3200 mg/l to 100 mg/l, while hardness has decreased from 300 ppm to 40 ppm. The results in Table 1 show the effectiveness of the AETM in treating the dyeing effluents. Our AETM technology can treat 25,000 liters – 2,00,000 liters of effluent per day

AETM Case Study 2: Municipal Sewage Treatment
The municipal sewage has a characteristic color, along with high chemical oxygen demand. AETM provides technologically sound, economic, and sustainable smart solution for treating the municipal sewage and offer the following solutions:
- Removal of the color and odors from the municipal sewage
- 90% water reuse
AETM uses following treatment methodologies for the municipal sewage:
- Preliminary treatment: Screening
- Primary treatment: COPR process
- Secondary treatment: AOPR method
Tertiary treatment: Final filtrations & reverse osmosis (RO) membrane (if needed)process

Raw and treated sewage characteristics.
| Parameter | Characteristics | Permissible Limit as per Govt. Norms | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sewage | Treated Water | ||
| pH | 7.71 | 6-7 | 6 – 8 |
| Nitrogen as N | 85 | 10 | 10 |
| BOD | 300 | 20 | 30 |
| COD | 650 | 150 | 250 |
| TSS | 350 | 20 | 25 |
| Chloride | 100 | 40 | 60 |
| TDS | 1200 | 100 | 2100 |
| Oil & Grease | 150 | 15 | 20 |
By considering the customers’ concern to see a demonstration of our treatment technology before placing an order, we have developed a 6KLD mobile demo unit that can travel to the customers’ location and facilitate an on-site demonstration. Our demo unit has successfully completed its first demo for a CETP at Erode, Tamil Nadu




Conventional ETP Results

1.Raw dyeing effluent.
- Primary Clarifier Output: Chemical Coagulation (Lime, Ferrous, A. Poly, HCl).
- Secondary Clarifier Output: Aeration-Biological Method.
- After Sand, Carbon, and Ultrafiltration (UF) (before RO)
Main Problem:
Since the treated quality is very poor, using it as the first feed for the RO unit quires daily cleaning and creates membrane chocking problem, leading to frequent membrane replacement
AETM Results

- Raw dyeing Effluent.
- COPR output: only 2 chemicals used (A. Poly & HCl)
- AOPR output
- Sand and carbon filtration output
UF output (before RO)
Main Advantage:
Since the output quality is highly improved, there is no need for daily cleaning of the RO unit, and hence the issues of membrane choking and frequent replacement are solved

